AMD Enterprise AI Suite: Open Infrastructure for Production AI#

In this blog, you’ll learn how to operationalize enterprise AI on AMD Instinct™ GPUs using an open, Kubernetes-native software stack. AMD Enterprise AI Suite provides a unified platform that integrates GPU infrastructure, workload orchestration, model inference, and lifecycle governance without dependence on proprietary systems. We begin by outlining the end-to-end architecture and then walk through how each component fits into production workflows: AMD Inference Microservice (AIM) for optimized and scalable model serving, AMD Solution Blueprints for assembling these capabilities into validated, end-to-end AI workflows, AMD Resource Manager for infrastructure administration and multi-team governance, and AMD AI Workbench for reproducible development and fine-tuning environments. Together, these building blocks show how to build, scale, and manage AI workloads across the enterprise using an open, modular, production-ready stack.
The AMD Enterprise AI Suite is designed for enterprise teams operating GPU infrastructure at scale, including Platform and Infrastructure teams that require predictable performance and governance across multi-node Instinct™ clusters; Data Scientists and ML Engineers who depend on reliable, self-service compute and reproducible development workflows; and Enterprise IT Leaders responsible for enforcing security, access control, and utilization policies while supporting rapid AI adoption.
Its core capabilities center on an open, modular architecture where each layer deploys independently via containers and Helm charts; a Kubernetes-native design that integrates directly with enterprise DevOps and MLOps pipelines; hardware-aware optimizations tuned for AMD CDNA™ architectures to maximize throughput and efficiency; unified observability through consistent telemetry, metrics, and logging; and enterprise security features such as RBAC, secrets management, and governance controls.
As shown in Figure 1, AMD Enterprise AI Suite integrates several foundational components that work together in production: AMD Inference Microservice (AIM) for high-performance, scalable model serving, AMD Solution Blueprints that provide validated generative and agentic AI workflows based on open, reproducible reference architectures, AMD Resource Manager for fine-grained resource governance, quotas, and workload policy enforcement across teams, and AMD AI Workbench as a unified environment for model development, fine-tuning, and managing AIM-based deployments. Combined, these components create a cohesive, production-ready AI stack engineered for performance, visibility, and control across the enterprise.
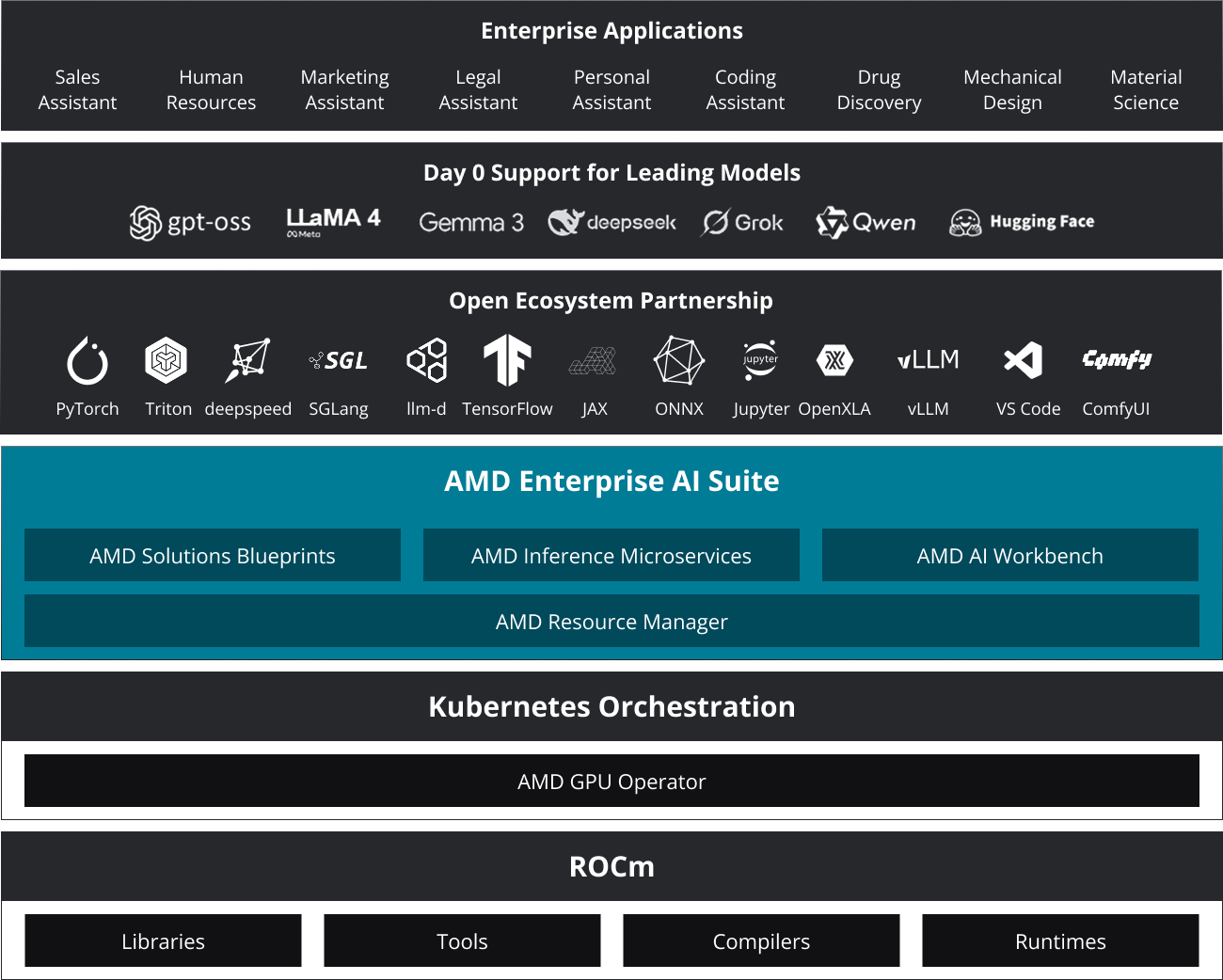
Figure 1: AMD Enterprise AI Suite
AMD Inference Microservices (AIMs): Production Ready Inference on AMD Instinct™ GPUs#
AMD Inference Microservices (AIMs) provide a modular framework for deploying and scaling inference workloads across heterogeneous clusters of AMD Instinct™ accelerators. Built natively on ROCm™ and Kubernetes, AIMs abstract hardware complexity while maximizing GPU utilization and throughput.
AIMs design principles focus on:
Ease of deployment through standard APIs and containers.
Hardware-specific optimization across AMD Instinct™ GPUs.
Scalability from a single GPU to multi-node clusters.
Observability with built-in metrics and health monitoring.
Architecture Overview#
AIMs simplify and accelerate inference on AMD Instinct™ by turning a complex, manual setup into a one-command deployment of validated models. They package validated profiles for AMD accelerators, delivering predictable performance, scalability, and seamless integration with open-source engines like vLLM. Figure 2 illustrates the AMD Inference Microservice (AIM) architecture, showing how optimized model runtimes, scalable serving layers, and Kubernetes-native orchestration integrate to deliver high-throughput, production-grade inference on AMD Instinct™ GPUs.
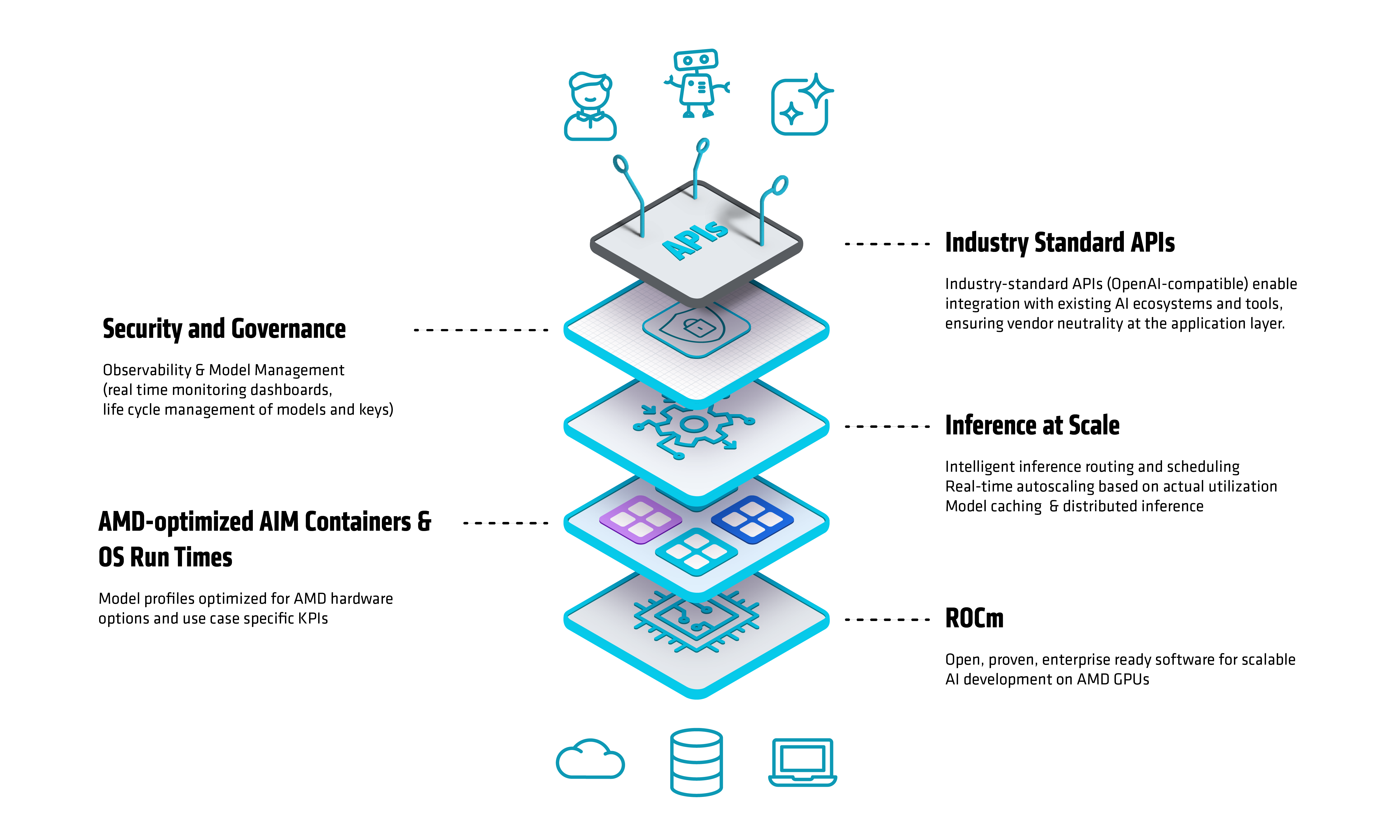
Figure 2: AMD Inference Microservice (AIM) Architecture
AIMs implement a microservices-based control plane that manages the full inference lifecycle:
Runtime Initialization Loads and validates containerized configurations
Hardware Detection Auto-discovers available AMD Instinct™ GPUs and health checks on each accelerator.
Profile Selection Matches model profiles to AMD Instinct™ GPUs (e.g., MI300X, MI325X) using validated performance templates.
Execution Command Generation Creates tuned runtime commands for tensor parallelism, precision (FP16, BF16, FP8), and communication optimizations.
Open-Source Inference Engine Support for popular open-source inference engines such as vLLM.
Model Caching & Memory Management Caches weights locally and dynamically manages GPU memory across sessions.
Observability & Autoscaling Exposes Prometheus-compatible metrics and scales pods through KServe autoscaling hooks.
AIMs expose OpenAI-compatible REST APIs, enabling immediate integration with existing LLM applications, chat frameworks, or agentic orchestration layers.
AMD Solution Blueprints: Accelerated Agentic and Generative AI Architectures#
AMD Solution Blueprints provide reference architectures that integrate AIMs with orchestration, retrieval, and application logic, delivering tested workflows for agentic and generative AI deployments. These blueprints serve as starting points and customers are encouraged to customize and extend them to fit specific use cases such as healthcare record summarization or financial forecasting, adapting the validated foundation to their own data, governance, and performance requirements.
Technical Composition#
An AMD Solution Blueprint typically includes:
Containerized AIMs module for serving inference workloads.
Data connectors for integrating enterprise knowledge bases or document stores.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines, including vector stores and embedding services.
Agent orchestration frameworks.
Monitoring & governance hooks for integration with AMD AI Workbench and AMD Resource Manager.
Initial Blueprints#
Agentic Translation#
Agentic machine translation pipeline with document ingestion and chunking for long-context document-level translation.
Incorporates arbitrary instructions for the translation, enabling enterprise rules and tone compliance.
LLM Chat Sandbox#
Modular playground for evaluating model behavior and prompt engineering.
Includes plug-in interfaces for custom retrieval modules and telemetry.
Local LLM Assistant for IDE#
Embeds AIMs powered LLMs in developer IDEs.
Supports context-aware suggestions, documentation generation, and inline code refactoring.
Financial Stock Intelligence#
A financial analysis tool that combines real-time stock data and technical indicators using an LLM to provide comprehensive stock insights.
Includes information from recent news, sustainability scores, and analyst recommendations.
AutoGen Studio Agentic Platform#
Create and configure AI agents with specific roles, personalities, and capabilities through a web interface.
Design complex conversation flows between multiple agents working collaboratively.
Seamless connection to AIMs for powering agent conversations.
View and debug agent conversations as they happen.
Pre-configured with a WebSurfer Agent Team ready for product comparison tasks.
Ecosystem & Infrastructure#
These blueprints are part of AMD broader ecosystem, where we collaborate with systems integrators, cloud and hardware partners, model developers, and tool providers to bring greater scalability and compatibility to developers everywhere.
Whether you deploy AMD certified systems in edge locations or in the cloud, AMD Solution Blueprints are infrastructure agnostic, but performance tuned for AMD hardware.
AMD Resource Manager: Cluster, Policy, and Governance Control Plane#
In large-scale AI operations, managing compute clusters, allocating quotas, controlling user access, and monitoring resource utilization all become complex and mission critical. Figure 3 shows the AMD Resource Manager interface, which provides a unified control plane that simplifies these tasks and centralized AI infrastructure governance.
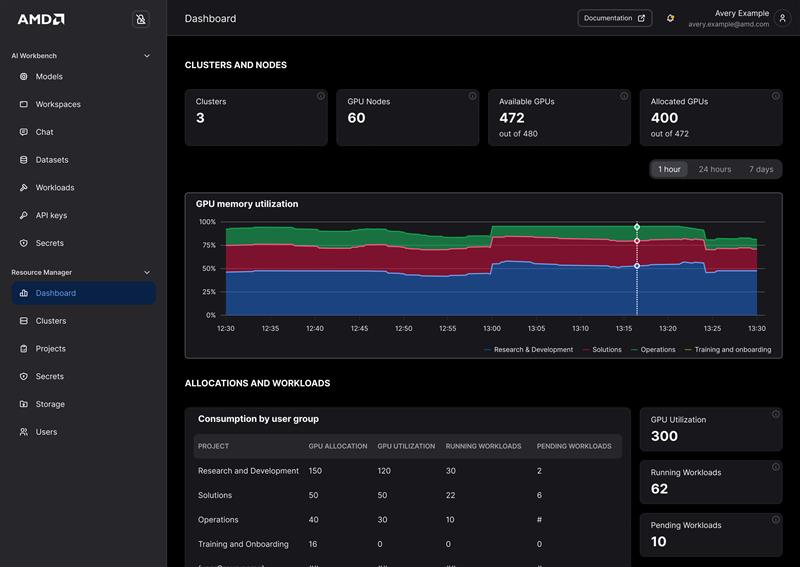
Figure 3: AMD Resource Manager User Interface
Key Capabilities#
1. Cluster & Infrastructure Visibility#
AMD Resource Manager delivers a unified cluster overview dashboard that provides real-time insights into cluster health, utilization, and capacity. Infrastructure administrators can seamlessly add, monitor, and manage on-prem and cloud compute clusters from a single intuitive console.
2. Workloads & Quotas Management#
Gain clear visibility into active workloads, and resource consumption bottlenecks. AMD Resource Manager simplifies project governance with built-in tools to create projects, define quotas, and enforce scheduling policies, ensuring fair and efficient use of compute resources across teams.
3. User & Role Management#
Empower teams with secure, role-based access. AMD Resource Manager enables administrators to create users, assign roles, integrate SSO, and manage invitations from a centralized interface.
4. Secrets & Access Control#
Protect sensitive data with centralized management of credentials, API keys, and secrets. AMD Resource Manager enforces fine-grained access controls to help enterprises maintain security and compliance.
AMD Resource Manager ensures that compute resources are always used efficiently, predictably, and securely, which is critical for multi-team / multi-tenant enterprise environments.
By integrating with AMD’s broader AI platform ecosystem, AMD Resource Manager helps organizations:
Govern compute clusters and infrastructure at scale.
Manage user roles and projects, including quotas and access.
Track workloads and monitor utilization across clusters.
Simplify setup for AI teams via templated workflows and pre-configured environments.
Ensure that infrastructure investment is optimized, and AI workloads don’t get bottlenecked by resource constraints.
AMD AI Workbench: AIMs Management UI, AI Developer Tooling and Workspaces#
AMD AI Workbench is a unified interface to manage, develop, fine-tune, and deploy AI workloads at scale. As shown in Figure 4, the Workbench interface offers AI practitioners and data scientists a cohesive environment that streamlines the full AI lifecycle from experimentation to deployment.
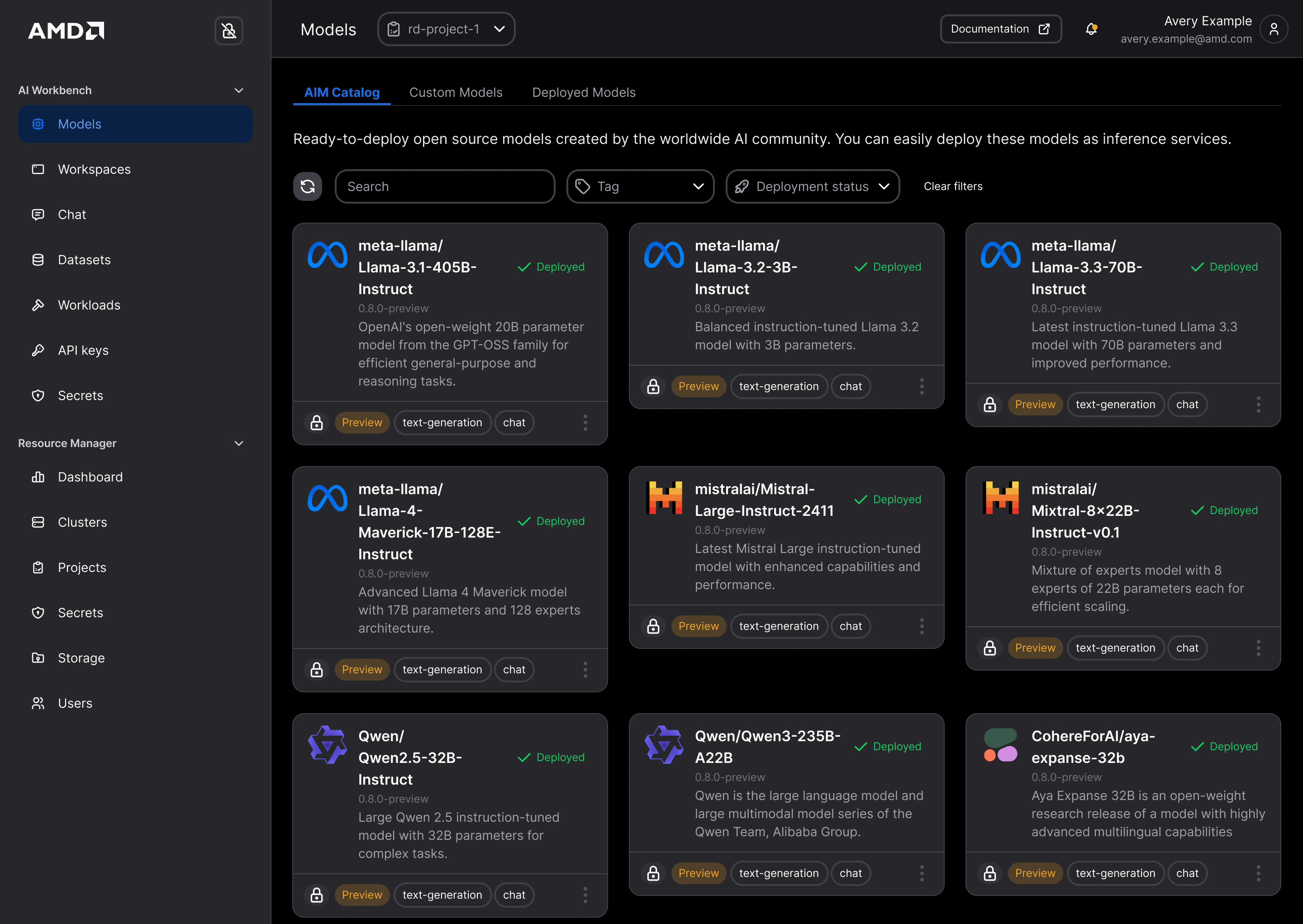
Figure 4: AMD AI Workbench Interface
Key Capabilities in AMD AI Workbench#
1. AIMs Catalog#
The AIMs catalogue is onboarded to the AI Workbench and the user can browse, deploy and interact with AIMs. API key management allows sharing the deployed AIMs inference API with external users and applications and monitor the utilization.
2. AI Workspaces#
Launch pre-configured development workspaces optimized for AMD compute to accelerate experimentation. Select the desired amount of GPU resources, targeted base image and deploy e.g. VScode or JupyterLab to get started with development on AMD GPUs.
3. Training & Fine-Tuning#
Customize base models with your own data to address specific enterprise use cases. Choose between a low code UI with pre-set hyperparameters “recipes” created by AMD AI experts or take advantage of a larger selection for the expert users of reference AI workloads for Kubernetes CLI.
4. Chat & Compare#
Interactively test AIMs and custom models through a chat interface and compare outputs side-by-side to quickly get a gist of performance.
5. GPU-as-a-Service#
Enable teams to self-provision GPU resources while administrators retain control through quotas and governance.
As AI adoption accelerates, the development, governance, and deployment of models become increasingly complex. AMD AI Workbench simplifies these challenges by:
Providing a single interface to manage the full AI lifecycle, from model exploration to deployment.
Ensuring developer productivity with ready-to-use workspaces and curated model assets.
Delivering resource control & scalability, allowing organizations to manage compute, teams, and budgets without bottlenecks.
Enabling rapid iteration, offering both GUI and CLI access so data scientists can experiment quickly while platform teams maintain governance.
Summary#
This blog outlined how the AMD Enterprise AI Suite delivers a unified, open, and performance-optimized foundation for running AI workloads on AMD Instinct™ GPUs. You saw how AMD Inference Microservice (AIM) delivers optimized model serving, how AMD Solution Blueprints provide validated workflow patterns, how AMD Resource Manager enforces multi-team governance, and how AMD AI Workbench enables reproducible development, together forming a unified, production-ready AI stack. These components enable enterprise teams to accelerate the path from prototype to production, whether deploying multi-node LLM inference, building agentic pipelines, or operating large GPU fleets with predictable performance and control.
Looking ahead, the team will continue expanding reference architectures, adding new AIM model profiles, extending governance capabilities in Resource Manager, and delivering deeper integrations across the suite. For a deeper look at the inference layer introduced here, see the companion AMD Inference Microservice (AIM) blog. Future posts will build on both blogs with additional guidance, best practices, and validated designs to help enterprises scale AI confidently on AMD hardware.
Get Started#
AMD Inference Microservices (AIMs): AIMs are open-source and available now. Developers can start deploying optimized inference workloads on AMD Instinct™ GPUs: AIMs catalog.
AMD Solution Blueprints: visit the AMD Solution Blueprints catalog and download reference code and documentation.
Install the AMD Resource Manager and AMD AI Workbench.
Visit the AMD Enterprise AI Suite product page
Visit the AMD Enterprise AI Suite developer page
Disclaimers#
Third-party content is licensed to you directly by the third party that owns the content and is not licensed to you by AMD. ALL LINKED THIRD-PARTY CONTENT IS PROVIDED “AS IS” WITHOUT A WARRANTY OF ANY KIND. USE OF SUCH THIRD-PARTY CONTENT IS DONE AT YOUR SOLE DISCRETION AND UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES WILL AMD BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR ANY THIRD-PARTY CONTENT. YOU ASSUME ALL RISK AND ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY DAMAGES THAT MAY ARISE FROM YOUR USE OF THIRD-PARTY CONTENT.