ROCm Becomes a First-Class Platform in the vLLM Ecosystem#

As the generative AI ecosystem matures, vLLM embraces a multivendor ecosystem. The quality of support across hardware platforms becomes a defining priority: developers expect consistent, high-performance behavior no matter which GPU they choose. Today, we are proud to announce a major realization of that vision: AMD ROCm™ is now a first-class platform in the vLLM ecosystem.
This achievement represents months of dedicated engineering and cross-team collaboration between AMD and the broader vLLM community. Together, we broke down silos, coordinated across complex dependencies, and delivered what users have been asking for: a seamless, “it just works” experience on AMD hardware.
In this blog, we first list the new capabilities and performance optimizations in recent vLLM releases, then showcase major milestones that significantly improve the developer experience—from seamless pip install vllm, to stronger upstream CI stability, to official Docker images for both vLLM and vLLM-omni. Together, these advancements unlock the full performance potential of AMD Instinct™ MI300 and Instinct MI350 GPUs for AI inference.
vLLM Core (v0.12.0 and v0.13.0): New Features and Performance Optimizations#
Looking back, with the recent vLLM v0.12.0 and v0.13.0 releases, ROCm has raised the bar, bringing new features and substantial performance improvements.
Quantization: Delivered major FP8, FP4, and low-bit improvements including native AITER FP8 kernels, fused LayerNorm/SiLU FP8 block quantization, Triton ScaledMM fallback, MXFP4 w4a4 MoE inference, FP8 MLA decode, and fused RMSNorm quantization.
Performance Optimizations: Unlocked higher throughput with optimized KV cache + assembly Paged Attention, AITER sampling ops, removal of DeepSeek MLA D2D copies, fused MoE binary masking, and fastsafetensors loading.
New Capabilities: Added support for DeepSeek v3.2 + SparseMLA, Whisper v1 with AITER attention, sliding window attention, multi-token prediction for AITER MLA, and non-gated MoE architectures.
Broader Hardware Support: Extended bitsandbytes quantization to warp size 32 GPUs like RDNA RX 7900 XTX.
For details, see the v0.12.0 release notes and v0.13.0 release notes.
vLLM Core (v0.14.0): A New Standard for Stability#
With the release of v0.14.0, the ROCm experience in the core vLLM project has reached an exciting new level of maturity. The community’s dedication is clearly paying off, transforming ROCm support into a proactive, forward-looking experience that continues to elevate the ecosystem, driven by a strong focus on CI stability, Docker image and Python wheel availability, and a streamlined installation experience. These improvements make getting started with vLLM easier, faster, and more reliable than ever.
ROCm Improvements in v0.14.0#
In vLLM v0.14.0, ROCm introduces several key enhancements [1], including AITER RMSNorm fusion, MTP support for AITER MLA, the moriio connector, upstream integration for xgrammar, and critical accuracy and performance regression fixes. Together, these upgrades continue to expand ROCm’s performance and capability footprint within the vLLM ecosystem.
Most notably, Docker and wheel build pipelines are introduced which directly benefit AMD developers and users:
Faster Builds: ROCm wheel pipeline with sccache for significantly reduced build times.
Release Pipeline: Added ROCm image build to the official release pipeline
For details, see the v0.14.0 release notes.
CI Reliability You Can Trust#
Over the past two months leading to this release, contributors worked intensively to enable numerous previously failed or skipped tests in the AMD CI pipeline, strengthening upstream reliability. The result is a robust testing environment where ROCm support is continuously validated.
In mid-November 2025, only 37% of the vLLM test groups in the AMD CI pipeline were passing. As of mid-January 2026, 93% of the vLLM AMD test groups are succeeding with daily maintenance of regressions and the goal of 100% within reach.
A new public project in upstream vLLM allows the open-source community to engage in our CI activities. Additionally, we are actively collaborating with the maintainers to transition our CI pipeline to fully coordinate with vLLM CI by gating test groups upstream and adding labels to selectively trigger the CI pipeline.
Official Docker Image Releases#
Official ROCm-enabled Docker images for vLLM are now available with release v0.14.0, ensuring seamless deployment for AMD GPUs.
Quick Start with Docker#
The vLLM ROCm OpenAI Docker image now supports the standard vllm serve entrypoint. Just use the ROCm Docker image with AMD-compatible docker run arguments, and you’re ready to go.
Figure 1 below (Source: vllm.ai) lists the Stable ROCm Docker quick start command [2].
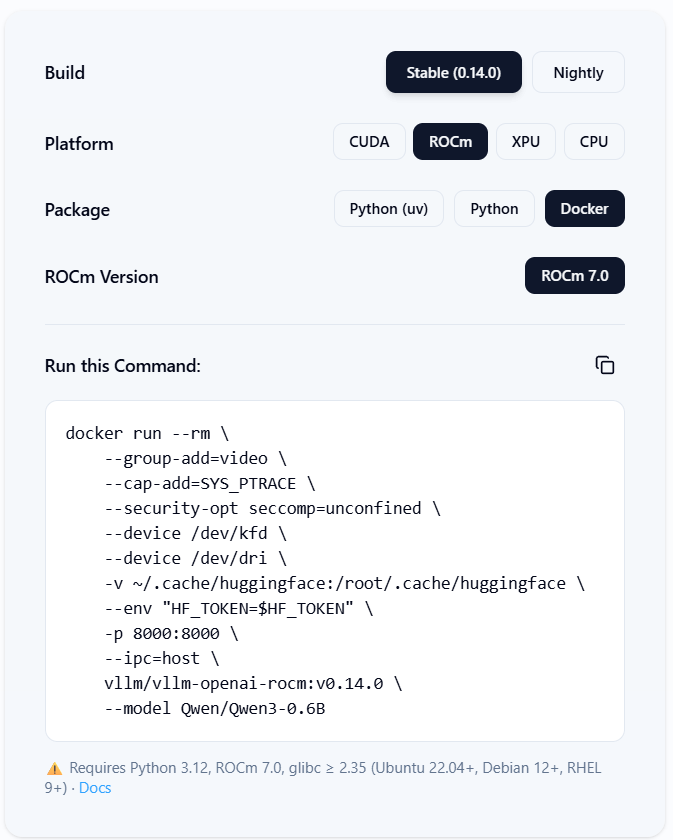
Figure 1: Stable vLLM ROCm Docker quick start#
docker pull vllm/vllm-openai-rocm:v0.14.0
docker run --rm \
--group-add=video \
--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE \
--security-opt seccomp=unconfined \
--device /dev/kfd \
--device /dev/dri \
-p 8000:8000 \
--ipc=host \
-e “HF_TOKEN=$HF_TOKEN” \
-e VLLM_ROCM_USE_AITER=1 \
-v ~/.cache/huggingface:/root/.cache/huggingface \
vllm/vllm-openai-rocm:v0.14.0 \
--model Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B
Easy Installation with vLLM Wheel#
The installation process has been streamlined with an official ROCm wheel release pipeline. Figure 2 below (Source: vllm.ai) lists the Stable ROCm wheel installation command.
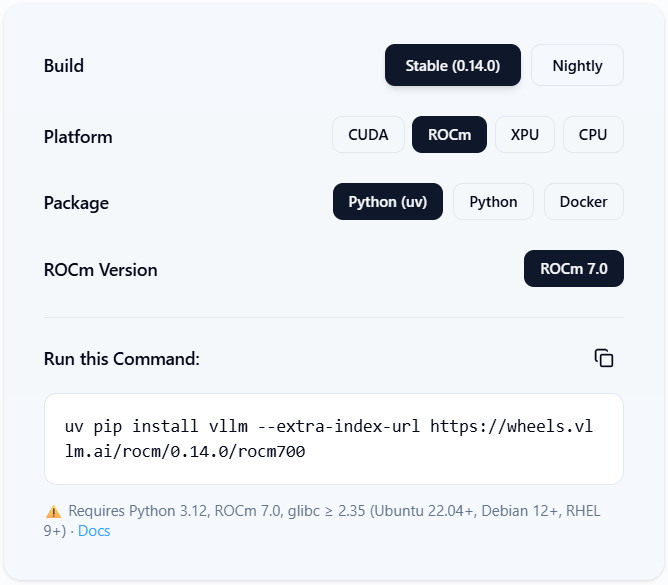
Figure 2: Stable vLLM ROCm wheel quick installation#
uv pip install vllm --extra-index-url https://wheels.vllm.ai/rocm/
This will install the wheel of the latest vLLM version which is ROCm 7.0 compatible. This wheel is compatible with Python 3.12, ROCm 7.0 and glibc >= 2.35.
If you would like to install a specific version of vLLM and variant, you can install it using a URL that has the following format:
uv pip install vllm --extra-index-url https://wheels.vllm.ai/rocm/<version>/<rocm-variant>/
Example:
uv pip install vllm --extra-index-url https://wheels.vllm.ai/rocm/0.14.0/rocm700/
This milestone reflects our shared commitment to making ROCm a first-class platform in the vLLM ecosystem. Switching from CUDA to ROCm is now seamless, enabling users to confidently leverage the powerful Instinct MI-series GPUs.
vLLM-omni: High-Performance Omni-Modality on AMD#
vLLM-omni is the “easy, fast, and cheap omni-modality” [3] model serving and inference framework introduced in November 2025.
When vLLM-omni launched, the community ensured that AMD users sat in the front row. vLLM-Omni provides robust, production-ready support for AMD ROCm-powered GPUs, bringing high-performance omni-modality model serving to AMD hardware. The framework has been rigorously validated on the AMD Instinct MI300 GPUs and AMD Instinct MI350 GPUs (gfx942 and gfx950 architectures) and supports the broader range of AMD GPUs compatible with vLLM.
Day-0 ROCm Support#
The community delivered Day-0 ROCm support, ensuring that from the moment vLLM-omni went live in November 2025, it was fully ready for AMD hardware. This commitment to inclusivity from day one reflects the open-source spirit that drives the vLLM ecosystem.
Hardware Validation & Support#
Validated GPUs: AMD MI300/MI350 GPUs (gfx942, gfx950 architectures)
Target Hardware: AMD MI300X/MI325X/MI350X/MI355X and other ROCm-compatible GPUs
Production-Ready Infrastructure#
CI Enablement: Thanks to upstream collaboration, a dedicated ROCm CI pipeline went live on December 29, 2025, ensuring every commit is tested against AMD silicon to prevent regressions and guarantee reliability for production deployments.
Official Docker Image: As of January 6, 2026, users no longer need to build from source. The first pre-built official ROCm-enabled vLLM-omni Docker image is available directly from Docker Hub.
Image location: Docker Hub (vllm/vllm-omni-rocm)
Tag:
vllm/vllm-omni-rocm:v0.12.0rc1Version-tagged: to indicate the underlying vLLM release (e.g.,
v0.12.0rc1)
ROCm Configurations#
Dedicated configuration files tuned specifically for ROCm deployments ensure optimal performance out of the box (Optimized for MI325 GPUs in CI/CD environments):
vllm_omni/model_executor/stage_configs/rocm/qwen2_5_omni.yaml
vllm_omni/model_executor/stage_configs/rocm/qwen3_omni_moe.yaml
Full Model Support on ROCm#
All vLLM-Omni models are fully compatible with ROCm, including:
Qwen2.5-Omni: Full support for multi-stage architecture (thinker → talker → code2wav)
Qwen3-Omni-MoE: Tensor parallelism support for Mixture-of-Experts models
Diffusion models: Including text-to-image generation
Multi-modal models: Complete audio, image, video, and text processing pipelines
Supported Input and Output Modalities#
Model |
Input Modalities |
Output Modalities |
|---|---|---|
Qwen2.5-Omni |
Text, Image, Audio, Video |
Text, Audio |
Qwen3-Omni |
Text, Image, Audio, Video |
Text, Audio |
Qwen-Image |
Text, Image |
Image |
Z-Image |
Text, Image |
Image |
Get Started in Seconds#
We want you to spend time building applications, not configuring environments. Pull the official ROCm-enabled Docker image and start serving models today.
docker pull vllm/vllm-omni-rocm:v0.12.0rc1
docker run --rm \
--group-add=video \
--ipc=host \
--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE \
--security-opt seccomp=unconfined \
--device /dev/kfd \
--device /dev/dri \
-p 8091:8091 \
-e “HF_TOKEN=$HF_TOKEN” \
-v ~/.cache/huggingface:/root/.cache/huggingface \
vllm/vllm-omni-rocm:v0.12.0rc1 \
vllm serve --model Qwen/Qwen3-Omni-30B-A3B-Instruct --omni --port 8091
Summary#
The vLLM ecosystem has reached an important milestone: AMD ROCm™ is now fully integrated as a first-class platform, delivering consistent, high-performance inference across AMD Instinct™ MI300 and MI350 GPUs. This progress reflects months of deep engineering collaboration between AMD and the vLLM community, all driven by a shared commitment to a seamless, open-source developer experience. In this blog, we highlight the new quantization features, performance optimizations, and expanded model capabilities added in recent releases, followed by the foundational improvements that make vLLM easier to adopt: pip-installable packages, stronger upstream CI stability, and official Docker images for both vLLM and vLLM-omni.
This milestone builds on ongoing vLLM community efforts to optimize inference on AMD hardware. For additional insights into specific deployment strategies and performance tuning techniques, see our related blog posts on multimodal inference optimization [4], MoE parallelism strategies [5] and vLLM 0.9.x performance tuning [6].
Looking ahead, our work doesn’t stop here. In the coming months, we will focus on:
Improving developer experience by enabling nightly Docker builds and wheels to support Python-only installation.
Unlocking Graph-capture Performance for vLLM-omni
Kernel Improvements for vLLM-omni
Bringing broader support to AMD Radeon™ consumer GPUs.
Call to Action: Have a feature request? Join the conversation on GitHub Issues or tag us on the vLLM Slack.
Acknowledgements#
Making ROCm a first-class platform in the vLLM ecosystem was a major collaborative effort across many teams. The authors are deeply grateful to the AMD collaborators — Satya Ramji Ainapurapu, Randall Smith, Alexei Ivanov, Qiang Li, Charlie Fu, Divakar Verma, Andreas Karatzas, Yida Wu, Ryan Rock, Matt Wong, Micah Williamson, Omkar Kakarparthi, Divin Honnappa, Keerthana Bidar — and the broader ROCm organization, as well as Kevin Luu, Roger Wang, Hongsheng Liu, Simon Mo, and the vLLM and vLLM‑Omni maintainers. This milestone shows how fast an open source project moves when we build together.
References#
[1] vLLM v0.14.0 release note and milestone
[4] Accelerating Multimodal Inference in vLLM (One-Line Optimization)
[5] The vLLM MoE Playbook (Guide to TP, DP, PP, and Expert Parallelism)
[6] Accelerated LLM Inference on AMD Instinct™ GPUs (VLLM 0.9.x)
Disclaimers#
Third-party content is licensed to you directly by the third party that owns the content and is not licensed to you by AMD. ALL LINKED THIRD-PARTY CONTENT IS PROVIDED “AS IS” WITHOUT A WARRANTY OF ANY KIND. USE OF SUCH THIRD-PARTY CONTENT IS DONE AT YOUR SOLE DISCRETION AND UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES WILL AMD BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR ANY THIRD-PARTY CONTENT. YOU ASSUME ALL RISK AND ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY DAMAGES THAT MAY ARISE FROM YOUR USE OF THIRD-PARTY CONTENT.